🔱 Codebase Overview
Eask consists of two components: a command-line tool (the Eask CLI), and Elisp scripts.
The CLI, is used to find the corresponding lisp file and feed it into the Emacs executable. It would parse all options and convert them to Emacs understandable options on the lisp scripts end. It is written in plain JavaScript, the main file is located in src/util.js.
The Elisp scripts, is used to do the actual execution for each command that passes through the CLI. All commands are split into its file and are organized in the lisp folder. It is written in plain Emacs Lisp, the main file is located in lisp/_prepare.el.
The yargs command file is written in JavaScript, and located under the cmds
folder. Each file under, will be named with convention [command_name].js. This
file should define basic command-line parsing rules and correctly prepare data
to feed the Emacs session.
Let’s look at the file cmds/core/archives.js:
exports.command = ['archives', 'sources']; // alias to sources
exports.desc = 'List out all package archives';
exports.handler = async (argv) => {
await UTIL.e_call(argv, 'core/archives');
};
This is a standard yargs command file, which contains all the information we need to pass it to the Emacs session.
- exports.command is the argument pattern, but it also accepts alias (array)
- exports.desc is the command description
- exports.handler is an asynchronous function that handles command execution
- UTIL is a global variable that points to the
src/util.jsmodule. 'core/archives'is the elisp file under lisp folder (without.elextension).
eask is a JavaScript file that holds all our global options.
yargs
.usage('Usage: eask <command> [options..]')
.help(
'help',
'Show usage instructions.'
)
.options({
'global': {
description: `change default workspace to ~/.eask/`,
alias: 'g',
type: 'boolean',
},
})
...
For local options, please use exports.builder and specify under its
command file.
See yargs/docs/advanced.md, the official documentation for more information and getting a better explanation would help!
Elisp scripts are located under the lisp folder and will wait to get called by the CLI. All Elisp scripts are written in Emacs Lisp and should have a similar structure below:
(let ((dir (file-name-directory (nth 1 (member "-scriptload" command-line-args)))))
(load (expand-file-name "_prepare.el"
(locate-dominating-file dir "_prepare.el"))
nil t))
(eask-start
(message "PWD is %s" default-directory))
See Development API section for more information!
There are three places you need to look into it:
easkfile at the root of the projectcmdsfolder with all available commandslispfolder with all elisp code
eask is the node entry, and the main yargs definition! cmds and lisp
folders are command files that correspond to each other.
Eask is executed this way:
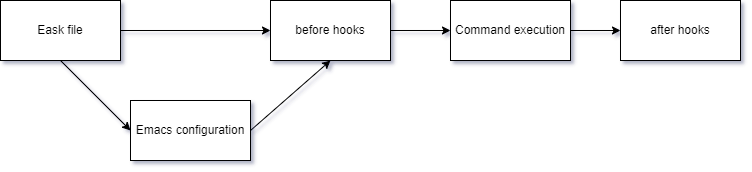
- Eask environment builds sandbox and reads Eask file information
- Emacs configuration is only being executed when
-goption is enabled - before hooks are hooks run before command task
- command execution is the primary command task
- after hooks are hooks run after command task
